What is driving so much interest in IPOs?
Think of it as a virtuous cycle. When the market sees investors making gains in IPOs, many more participants apply, leading to massive oversubscription. This in turn causes even more FOMO (fear of missing out), leading to hefty premiums on listing day.
Another reason is the steady increase in the number of demat accounts. India had just 21 million demat accounts in FY13 and 41 million in FY20. Then came the pandemic and the stock market surge, and in just 18 months (as of Q2 FY22) there were 70 million demat accounts in India. Around 29 million were added in the past 18 months alone, nine million more than in the seven years from FY13 to FY20!
(Graphics: Rahul Awasthi/ETtech)
Why the craze for new-age companies?
One reason for this is that these firms — , Paytm, Policybazaar, Nykaa, etc. — are household names. But the main clue lies in Angel Broking’s Q2 FY22 investor presentation, which states that the average age of a new demat account holder is now 29, down from 31. Younger people are more likely to invest in tech-led firms.
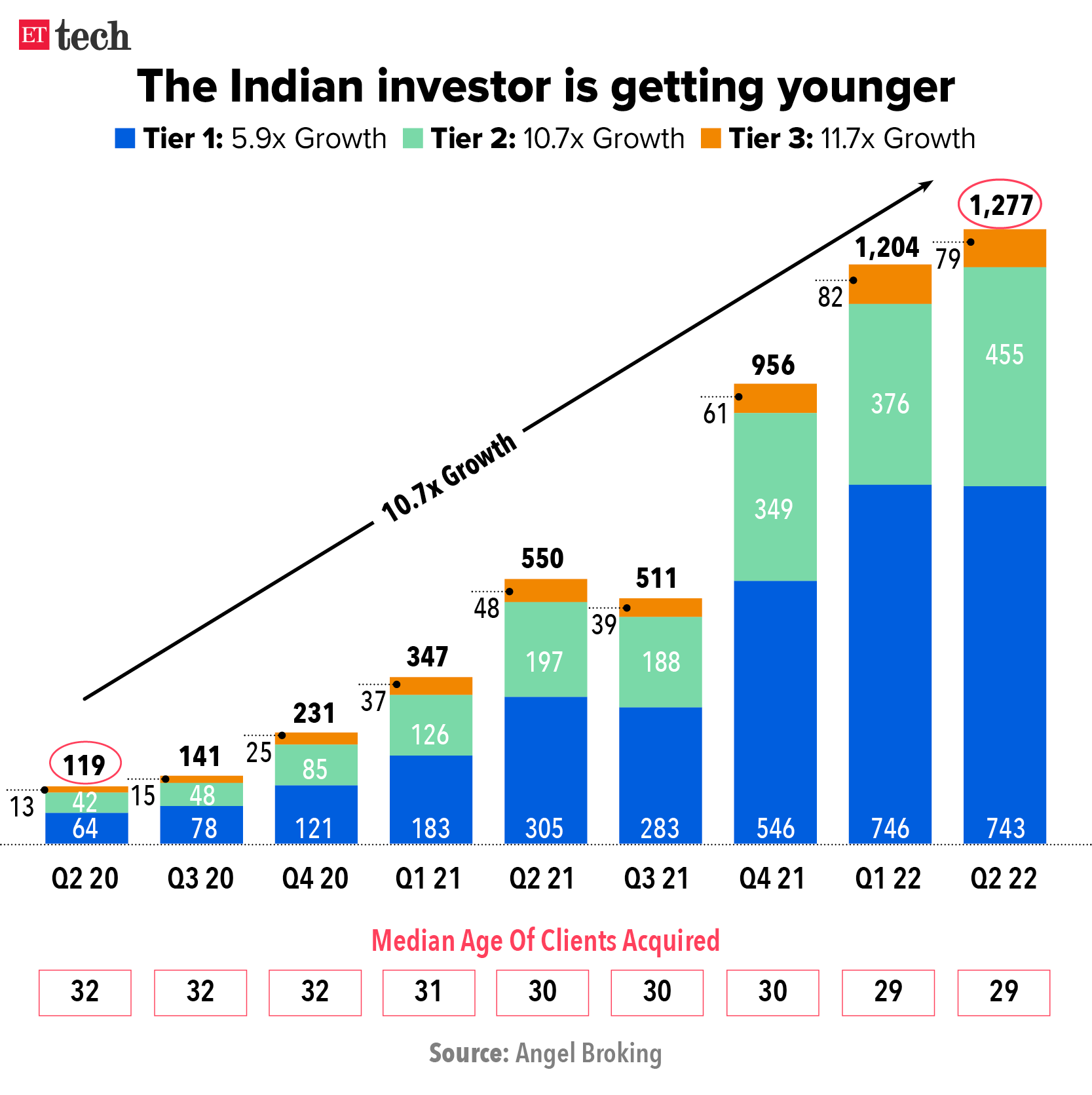 ETtech
ETtech
There has also been a tectonic shift in IPO markets — one that is not talked about.
Let’s rewind to 2007 — the fresh issue component of the average IPO was 94% and the offer for sale (OFS) component was just 6%. In a fresh issue, the money goes to the firm, while in the OFS, money goes to shareholders who dilute or cash out their stakes.
 ETtech
ETtechOne of the principles of being a shareholder is: what’s the benefit of investing in a company if it doesn’t receive the funds? Of course, it can be said that the company is new-age and doesn’t need funds. In that case you need to question why you are funding someone else’s exit at frothy valuations, since IPOs always come in euphoric periods — 2007-08, 2010, 2017-18 and 2021.
This also has to do with the changing structure of India’s corporate firms. A decade or so ago, businesses were funded with their own money or debt (bank loans). But thanks to the startup culture, advancements in tech, and abundant liquidity, new-age founders now have the benefit of private equity and venture capital (PE/VC) investments.
Consequently, no one is taking — or wants to take — the slow route in business. Everyone wants to scale up, and PE/VCs demand this. They typically invest well before the company is listed and usually sell some or all their shares in IPOs.
So, the typical investment lifecycle of a PE/VC-backed company going for an IPO looks like this: Promoters > Employees (stock options) > PE/VC/angel investors > Pre-IPO investors > Listed market investors and retail investors.
Shareholding structure isn’t the only change brewing in IPO markets.
Food delivery company Zomato, which is backed by major PE/VCs,
was listed on the bourses with heavy subscriptions, much fanfare, and
a good listing premium. It is not a traditional business with “real” assets. It doesn’t own restaurants or delivery vehicles. It just connects restaurants and customers and fulfills orders through gig workers.
Zomato’s successful listing and the massive interest in it signaled to all other startups that the Indian markets have matured and are ready for new-age companies. The current market euphoria has also helped as companies are tapping the markets at astronomical — and sometimes illogical — valuations.
 ETtech
ETtechLet’s talk numbers:
- In 2015, there were no IPOs by new-age firms.
- In 2019, there were 16 IPOs and two of these were by new-age companies — Affle India and IndiaMart Intermesh.
- In 2020 there were 15 IPOs, of which only one was by a new-age business — Route Mobile.
- In 2021, there were 42 IPOs as of September 30. Five of these were by new-age companies — Zomato, CarTrade, EaseMyTrip and Nazara Technologies. And four more startups have launched IPOs since then — Nykaa, Fino Payments Bank, Policybazaar and Paytm.
Many others have filed for IPOs or plan to soon, including Pharmeasy, Delhivery, Snapdeal, Byjus, Pepperfry, Mobikwik, Inmobi and RateGain.
IPOs in the US
These numbers are dwarfed by those in the US markets. As of October 18, 777 US IPOs, including blank-cheque companies or SPACs, have raised a total of $249.22 billion this year, according to Dealogic.
It’s even more important then to remember that IPOs are a mania, and that they come in bunches during times of euphoria. After all, one in four companies that went public during the 2010 boom no longer exist. And more than a decade later, half those companies are trading below their issue price.
Not all companies planning IPOs will be successful. One must read the draft IPO prospectus, understand the business and the growth runway ahead before investing. Don’t fall for narratives.
The author is chief operating officer at JST Investments. The companies mentioned above are strictly not recommendations. Graphics by Rahul Awasthi/ETtech.


























